🔐Blockchain Security Audits
Smart Contract Audits
Our Solidity smart contracts are audited by trusted 3rd party security teams.
Our current Auditor is Solidity Finance. Here is a link to our latest Smart contract audits: https://solidity.finance/audits/EndersgateNFT/
Smart Contract Audit Report
AUDIT SUMMARY
 Endersgate is a new NFT collection where users use can claim and exchange NFTs.
Endersgate is a new NFT collection where users use can claim and exchange NFTs.
For this audit, we reviewed the following contracts on the team's GitHub repository:
EndersPack contract at commit 72697f09001683be6c9b832692c1b0894ed6d37e.
EndersGate contract at commit 839e1f8b3d6487cd29f9ff1f91c99863debb4149.
ExchangeERC1155 contract at commit 63dfe757da194d7148a1ad9ded4d9540c96b8eb0.
AUDIT FINDINGS
Please ensure trust in the team prior to investing as they have some control in the ecosystem. Date: March 22nd, 2022. Updated: April 1st, 2022 to address changes made to the EndersPack contract as well as add the ExchangeERC1155 and EndersGate contracts to the audit scope. Updated April 6th, 2022 to address changes made to the EndersPack contract.
Finding #1 - EndersPack - High (Resolved)Description: Contracts are permitted to call the
unpack()function. Risk/Impact: A malicious contract can be used to revert any Endersgate NFT unpacking that does not result in a favorable bonus NFT type, negating any intended randomness functionality. The contract could use this to extract more valuable or preferred bonus NFT types from NFT unpacking and leave other users with the less valuable or unpreferred rewards. Recommendation: The team should disallow contracts from calling theunpack()function or alternatively, redesign the unpacking mechanism to leverage chainlink for a secure source of randomness. Resolution: The team has implemented logic so that contracts cannot call theunpack()function.
Finding #2 - EndersPack - Informational (Partially Resolved)Description: Several functions are declared public, but are never called internally.
EndersPack.setState, EndersPack.setOptionSettings, EndersPack.setTokensForTypes, EndersPack.mint, EndersPack.mintBatch, EndersPack.setURI, EndersPack.setContractURI, EndersPack.setIpfsHashBatch, EndersGate.set, URIEndersGate.setContract, URIEndersGate.mint, EndersGate.mintBatch, EndersGate.totalSupplyBatch, EndersGate.setIpfsHashBatch, ExchangeERC1155.exchangeAllERC1155, ExchangeERC1155.safeWithdrawal, ExchangeERC1155.updateNftsToId,Recommendation: We recommend declaring these functions external for additional gas savings on each call. Resolution: The team has declared some functions external.
CONTRACT OVERVIEW
As the contract is developed with Solidity 0.8.x, it is protected from overflow/underflow attacks.
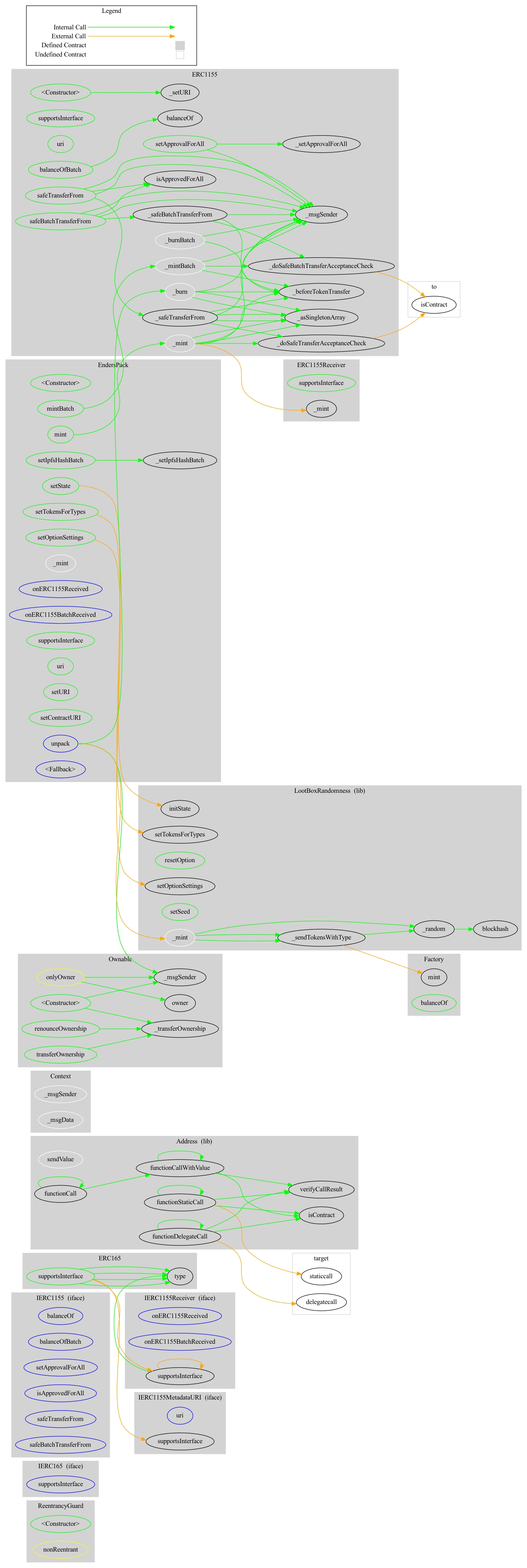
EndersPack Contract:
This contract enables the team to distribute EndersPack NFTs to users, which are used to claim reward NFTs from the _factoryAddress contract. The _factoryAddress contract is not within the scope of this audit, so we are unable to provide an assessment of the contract with regards to security.
All EndersPack NFTs belong to an NFT option group; each NFT option group contains specified NFT option types.
Users can unpack their Endersgate NFTs in order to be minted the base amount of each NFT option type within their EndersPack NFT option group; EndersPack NFTs are burned once used to claim a reward NFT.
Additionally, users are minted a pseudo-randomly selected bonus reward NFT as long as the EndersPack NFT's option group mint limit and the bonus NFT's option type limit have not been reached.
The previous block number, caller address, and seed value are used to determine the pseudo-randomly selected bonus NFT.
The owner can transfer ownership at any time.
The owner can mint EndersPack NFTs at any time.
The owner can change the _factoryAddress address, the number of NFT option groups, NFT option types within each option group, and seed value at any time.
The owner can change the NFT option group's mint limit, base amount, and NFT option type limit at any time.
The owner can change the token ID values corresponding to the NFT option types that are passed to the _factoryAddress contract.
The owner can set the contract URI and token URI prefix at any time
The owner can change all tokens' IPFS URL values at any time.
In the event that the address receiving an EndersPack NFT is a contract, the contract must have implemented the onERC1155Received() function in order to successfully receive the NFT.
ReentrancyGuard is utilized within the unpack() function to prevent re-entrancy attacks.
The contract complies with the ERC-1155 Multi-token standard.
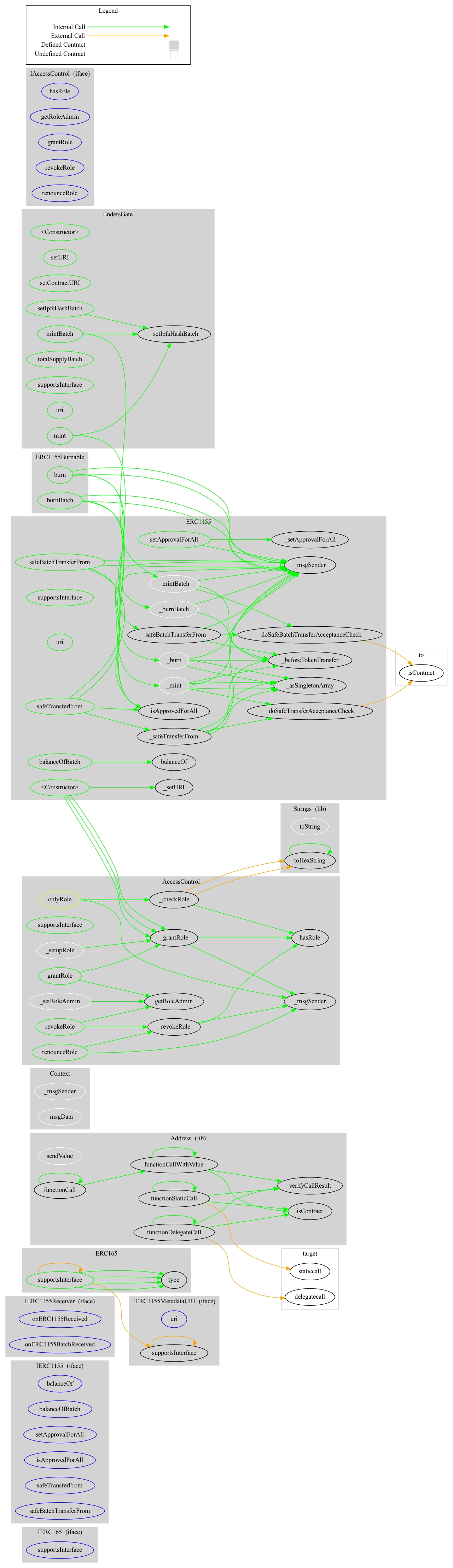
EndersGate Contract:
This contract enables the team to distribute EndersGate NFTs to users.
On deployment, the owner is granted the Default Admin role, URI Setter role, and Minter role.
A mint function is present in the contract and can be utilized only by the Minter role to mint any amount of any token ID to specified addresses, increasing the total supply at any time.
Any user can burn their own tokens to reduce the total supply.
Additionally, users can burn tokens from other addresses up to the amount of allowance they've been granted, also reducing the total supply.
The URI Setter role can set the contracts token URI prefix and contract URI at any time.
The URI Setter role can change all tokens' IPFS URL value at any time.
The owner can grant and revoke each role to any address at any time.
The contract complies with the ERC-1155 Multi-token standard.
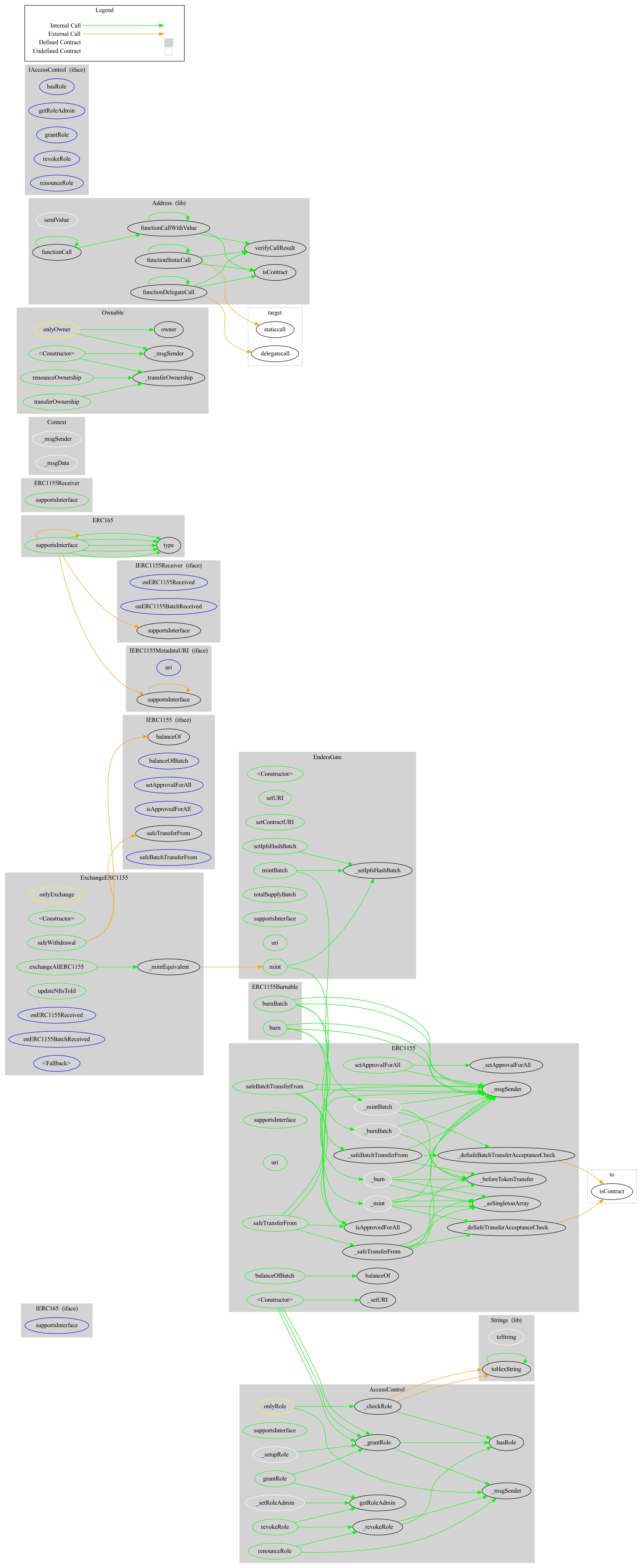
ExchangeERC1155 Contract:
This contract enables users to exchange NFTs from approved NFT collections for an equivalent amount of reward NFTs from an owner-defined contract address; the team should use caution as the approved NFT collection addresses and reward contract address are set on deployment and cannot be added to or changed.
The EndersGate contract is intended to be the reward contract address.
The collection address and ID of the NFT traded into the contract determines the NFT that the user receives from the reward contract address.
The owner can change which reward NFTs users receive for exchanged NFTs.
The owner can withdraw all NFTs within the contract at any time.
The owner can transfer ownership at any time.
AUDIT RESULTS
Arbitrary Jump/Storage Write
N/A
PASS
Centralization of Control
The team can mint EndersPack and EndersGate NFTs at any time.
WARNING
Compiler Issues
N/A
PASS
Delegate Call to Untrusted Contract
N/A
PASS
Dependence on Predictable Variables
A bonus reward NFT can be predicted as it is reliant on only the previous block.number, msg.sender, and the seed value; however, the likelihood of this along with its use for exploitation is very low.
WARNING
Ether/Token Theft
N/A
PASS
Flash Loans
N/A
PASS
Front Running
N/A
PASS
Improper Events
N/A
PASS
Improper Authorization Scheme
N/A
PASS
Integer Over/Underflow
N/A
PASS
Logical Issues
N/A
PASS
Oracle Issues
N/A
PASS
Outdated Compiler Version
N/A
PASS
Race Conditions
N/A
PASS
Reentrancy
N/A
PASS
Signature Issues
N/A
PASS
Unbounded Loops
N/A
PASS
Unused Code
N/A
PASS
Overall Contract Safety
PASS
EndersPack Contract

EndersGate Contract

ExchangeERC1155 Contract

ABOUT SOLIDITY FINANCE
Solidity Finance was founded in 2020 and quickly grew to have one of the most experienced and well-equipped smart contract auditing teams in the industry. Our team has conducted 1000+ solidity smart contract audits covering all major project types and protocols, securing a total of over $10 billion U.S. dollars in on-chain value. Our firm is well-reputed in the community and is trusted as a top smart contract auditing company for the review of solidity code, no matter how complex. Our team of experienced solidity smart contract auditors performs audits for tokens, NFTs, crowdsales, marketplaces, gambling games, financial protocols, and more!
Contact us today to get a free quote for a smart contract audit of your project!
WHAT IS A SOLIDITY AUDIT?
Typically, a smart contract audit is a comprehensive review process designed to discover logical errors, security vulnerabilities, and optimization opportunities within code. A Solidity Audit takes this a step further by verifying economic logic to ensure the stability of smart contracts and highlighting privileged functionality to create a report that is easy to understand for developers and community members alike.
HOW DO I INTERPRET THE FINDINGS?
Each of our Findings will be labeled with a Severity level. We always recommend the team resolve High, Medium, and Low severity findings prior to deploying the code to the mainnet. Here is a breakdown on what each Severity level means for the project:
High severity indicates that the issue puts a large number of users' funds at risk and has a high probability of exploitation, or the smart contract contains serious logical issues which can prevent the code from operating as intended.
Medium severity issues are those which place at least some users' funds at risk and has a medium to high probability of exploitation.
Low severity issues have a relatively minor risk association; these issues have a low probability of occurring or may have a minimal impact.
Informational issues pose no immediate risk, but inform the project team of opportunities for gas optimizations and following smart contract security best practices.
Last updated
Was this helpful?